Although this post is old and already answered, it can still be helpful to others so I will add my answer.
I came up with two ways for maintaining a relative position for elements in a Canvas
- MultiValueConverter
- Attached Properties
The idea is to provide two values (x,y) in range [0,1] that will define the relative position of the element with respect to the top-left corner of the Canvas. These (x,y) values will be used to calculate and set the correct Canvas.Left and Canvas.Top values.
In order to place the center of the element at a relative position, we will need the ActualWidth and ActualHeight of the Canvas and the element.
MultiValueConverter
The MultiValueConverter RelativePositionConverter:
This converter can be used to relatively position the X and/or Y position when binding with Canvas.Left and Canvas.Top.
public class RelativePositionConverter : IMultiValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object[] values, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (values?.Length < 2
|| !(values[0] is double relativePosition)
|| !(values[1] is double size)
|| !(parameter is string)
|| !double.TryParse((string)parameter, out double relativeToValue))
{
return DependencyProperty.UnsetValue;
}
return relativePosition * relativeToValue - size / 2;
}
public object[] ConvertBack(object value, Type[] targetTypes, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
Example usage of RelativePositionConverter:
A Canvas width and height are binded to an Image. The Canvas has a child element - an Ellipse that maintains a relative position with the Canvas (and Image).
<Grid Margin="10">
<Image x:Name="image" Source="Images/example-graph.png" />
<Canvas Background="#337EEBE8" Width="{Binding ElementName=image, Path=ActualWidth}" Height="{Binding ElementName=image, Path=ActualHeight}">
<Ellipse Width="35" Height="35" StrokeThickness="5" Fill="#D8FFFFFF" Stroke="#FFFBF73C">
<Canvas.Left>
<MultiBinding Converter="{StaticResource RelativePositionConverter}" ConverterParameter="0.461">
<Binding RelativeSource="{RelativeSource FindAncestor, AncestorType=Canvas}" Path="ActualWidth" />
<Binding RelativeSource="{RelativeSource Self}" Path="ActualWidth" />
</MultiBinding>
</Canvas.Left>
<Canvas.Top>
<MultiBinding Converter="{StaticResource RelativePositionConverter}" ConverterParameter="0.392">
<Binding RelativeSource="{RelativeSource FindAncestor, AncestorType=Canvas}" Path="ActualHeight" />
<Binding RelativeSource="{RelativeSource Self}" Path="ActualHeight" />
</MultiBinding>
</Canvas.Top>
</Ellipse>
</Canvas>
</Grid>
Attached Properties
The Attached Properties RelativeXProperty, RelativeYProperty and RelativePositionProperty:
RelativeXProperty and RelativeYProperty can be used to control the X and/or Y relative positioning with two separate attached properties.RelativePositionProperty can be used to control the X and Y relative positioning with a single attached property.
public static class CanvasExtensions
{
public static readonly DependencyProperty RelativeXProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("RelativeX", typeof(double), typeof(CanvasExtensions), new PropertyMetadata(0.0, new PropertyChangedCallback(OnRelativeXChanged)));
public static readonly DependencyProperty RelativeYProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("RelativeY", typeof(double), typeof(CanvasExtensions), new PropertyMetadata(0.0, new PropertyChangedCallback(OnRelativeYChanged)));
public static readonly DependencyProperty RelativePositionProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("RelativePosition", typeof(Point), typeof(CanvasExtensions), new PropertyMetadata(new Point(0, 0), new PropertyChangedCallback(OnRelativePositionChanged)));
public static double GetRelativeX(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (double)obj.GetValue(RelativeXProperty);
}
public static void SetRelativeX(DependencyObject obj, double value)
{
obj.SetValue(RelativeXProperty, value);
}
public static double GetRelativeY(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (double)obj.GetValue(RelativeYProperty);
}
public static void SetRelativeY(DependencyObject obj, double value)
{
obj.SetValue(RelativeYProperty, value);
}
public static Point GetRelativePosition(DependencyObject obj)
{
return (Point)obj.GetValue(RelativePositionProperty);
}
public static void SetRelativePosition(DependencyObject obj, Point value)
{
obj.SetValue(RelativePositionProperty, value);
}
private static void OnRelativeXChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (!(d is FrameworkElement element)) return;
if (!(VisualTreeHelper.GetParent(element) is Canvas canvas)) return;
canvas.SizeChanged += (s, arg) =>
{
double relativeXPosition = GetRelativeX(element);
double xPosition = relativeXPosition * canvas.ActualWidth - element.ActualWidth / 2;
Canvas.SetLeft(element, xPosition);
};
}
private static void OnRelativeYChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (!(d is FrameworkElement element)) return;
if (!(VisualTreeHelper.GetParent(element) is Canvas canvas)) return;
canvas.SizeChanged += (s, arg) =>
{
double relativeYPosition = GetRelativeY(element);
double yPosition = relativeYPosition * canvas.ActualHeight - element.ActualHeight / 2;
Canvas.SetTop(element, yPosition);
};
}
private static void OnRelativePositionChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (!(d is FrameworkElement element)) return;
if (!(VisualTreeHelper.GetParent(element) is Canvas canvas)) return;
canvas.SizeChanged += (s, arg) =>
{
Point relativePosition = GetRelativePosition(element);
double xPosition = relativePosition.X * canvas.ActualWidth - element.ActualWidth / 2;
double yPosition = relativePosition.Y * canvas.ActualHeight - element.ActualHeight / 2;
Canvas.SetLeft(element, xPosition);
Canvas.SetTop(element, yPosition);
};
}
}
Example usage of RelativeXProperty and RelativeYProperty:
<Grid Margin="10">
<Image x:Name="image" Source="Images/example-graph.png" />
<Canvas Background="#337EEBE8" Width="{Binding ElementName=image, Path=ActualWidth}" Height="{Binding ElementName=image, Path=ActualHeight}">
<Ellipse Width="35" Height="35" StrokeThickness="5" Fill="#D8FFFFFF" Stroke="#FFFBF73C"
local:CanvasExtensions.RelativeX="0.461"
local:CanvasExtensions.RelativeY="0.392">
</Ellipse>
</Canvas>
</Grid>
Example usage of RelativePositionProperty:
<Grid Margin="10">
<Image x:Name="image" Source="Images/example-graph.png" />
<Canvas Background="#337EEBE8" Width="{Binding ElementName=image, Path=ActualWidth}" Height="{Binding ElementName=image, Path=ActualHeight}">
<Ellipse Width="35" Height="35" StrokeThickness="5" Fill="#D8FFFFFF" Stroke="#FFFBF73C"
local:CanvasExtensions.RelativePosition="0.461,0.392">
</Ellipse>
</Canvas>
</Grid>
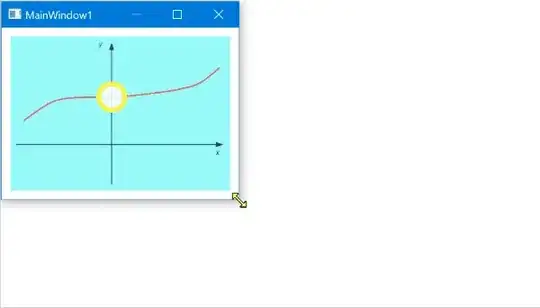
And hear is how it looks:
The Ellipse that is a child of a Canvas maintains a relative position with respect to the Canvas (and an Image).