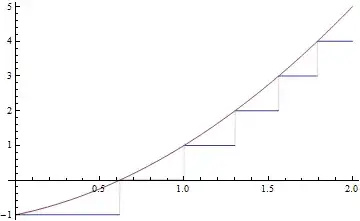
It seems to me that integrating the floor function gives you triangular numbers when the input is a whole number. So for those cases, you can use the triangular number formula but with $x-1$ instead of $x$ because the values are shifted to the right in this case.
$$\frac{(x-1)^2+(x-1)}2$$
Then to account for the portion of $x$ in between whole numbers, we do this:
$$\frac{(\lfloor x\rfloor-1)^2+(\lfloor x\rfloor-1)}2+(x-\lfloor x\rfloor)\lfloor x\rfloor$$
For negative integers, we have:
$$\frac{-(x-1)^2-(x-1)}2$$
And again we add on the non-integer portion:
$$\frac{-(\lfloor x\rfloor-1)^2-(\lfloor x\rfloor-1)}2-(x-\lfloor x\rfloor)\lfloor x\rfloor$$
It looks like the function for negative values of $x$ is the same as the function for positive values, but multiplied by $-1$. So if we want one function to be the answer for problem #1, we can have:
$$sgn(x)\left(\frac{(\lfloor x\rfloor-1)^2+(\lfloor x\rfloor-1)}2+(x-\lfloor x\rfloor)\lfloor x\rfloor\right)$$