In Mario Party, there exists two items (Double Dice, Mushroom), and I'm interested in seeing which is better probabilistically.
- Double Dice (X). Roll two dice, each ranging 1-10, then compute it's sum.
- Mushroom (Y). Roll one dice, ranging 1-10, then add +5 to the roll.
I'm looking for when: $P(X>Y)$, i.e, what is the probability that you will roll more with double dice v.s. mushroom. A general approach for when $P(X>Y)$ for any two discrete random variables would be appreciated as well. I found on other posts that this is equivalent to when $P(X-Y>0)$, but I'm not necessarily sure how to compute this quantity when X and Y are not normal distributions.
I've graphed the distributions for $X$ and $Y$ below for reference (note the scaling!)

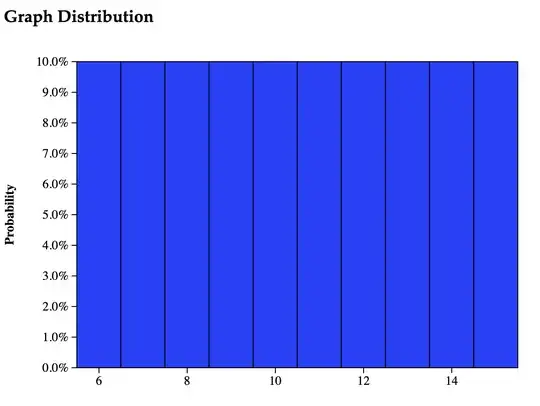 I don't have much experience with probability besides an introductory calculus based statistics course a few years ago, so any explanation will go a long way. Also, if there are names for these distributions and the distribution of $X-Y$, that would be appreciated as well.
I don't have much experience with probability besides an introductory calculus based statistics course a few years ago, so any explanation will go a long way. Also, if there are names for these distributions and the distribution of $X-Y$, that would be appreciated as well.
EDIT: My first idea in computing $P(X>Y)$ is to compute $$\sum_{k=2}^{20} P(X>k)$$ i.e, fixing $Y$ and adding up all the probabilities that $X$ is greater than some value of $k$. But I don't think this gives a valid probability distribution (sum is > 1) and am curious why this approach doesn't work.