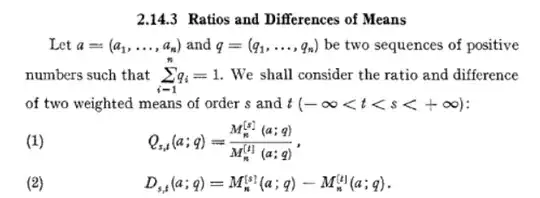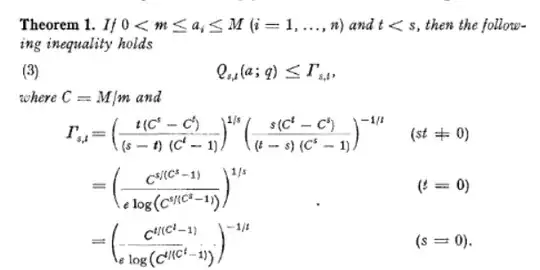We have the standard $1$ and $2$ norms $$ ||x||_1 := \sum_{i = 1}^n |x_i|, \qquad ||x||_2 := \sqrt{\sum_{i = 1}^n x_i^2}, $$ where $n \in \mathbb{N}$ and $x = (x_i)_{i = 1}^n \in \mathbb{Z}^n$. On the math.stackexchange page there are proofs of the inequalities $$ ||x||_2 \leqslant ||x||_1 \leqslant \sqrt{n}||x||_2. $$
I am interested in the weighted $1$ and $2$ norms $$ ||x||_1^w := \sum_{i = 1}^n w_i|x_i|, \qquad ||x||_2^w := \sqrt{\sum_{i = 1}^n w_ix_i^2}, $$ where $w = (w_i)_{i = 1}^n \in \mathbb{N}^n$.
Could you give me any reference in the literature to cite some results about these weighted norms in my scientific paper? In particular, I would like to know for them a proper version of the above inequalities. ''Proper'' means that the inequalities should be sufficiently optimal.
I guess that the theory of the norms $||\cdot||_1^w$ and $||\cdot||_2^w$ is quite classical to be already discussed somewhere. It is not correct and too long if I develop this theory from scratch in my paper. I cannot be the first author in the given research direction.
If it is difficult to find a reference in the literature and the result seems folklore, I will appreciate your help in formulating and proving the inequalities in question. Thanks in advance for any comment!
Note that $||x||_1^w = ||Wx||_1$ and $||x||_2^{w^2} = ||Wx||_2$, where $W := \mathrm{diag}(w_i)_{i = 1}^n$ and $w^2 := (w_i^2)_{i = 1}^n$. Consequently, $$ ||x||_2^{w^2} \leqslant ||x||_1^w \leqslant \sqrt{n}||x||_2^{w^2}. $$ Nevertheless, you may be able to propose more optimal inequalities.