To solve the inequality $\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2} \geq \dfrac{3x-1}{x+3}$, I multiplied in form of $x$ and got that $\begin{align*}(2x-1)(x+3) \geq (3x-1)(x+2)&\implies 2x^2+6x-x-3 \geq 3x^2+6x -x-2\\&\implies x^2 \leq -1\end{align*}$
I know that if we take it with basic knowledge there is no solution, but my question is what is the answer in complex numbers.
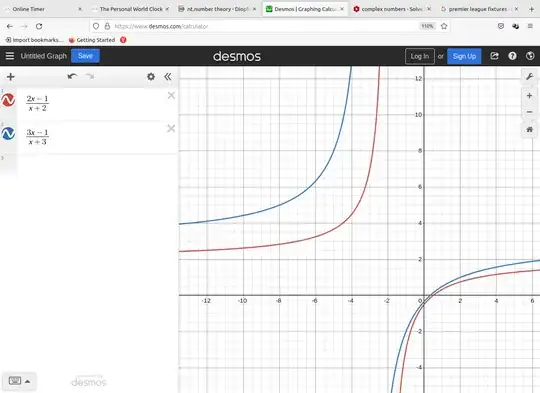
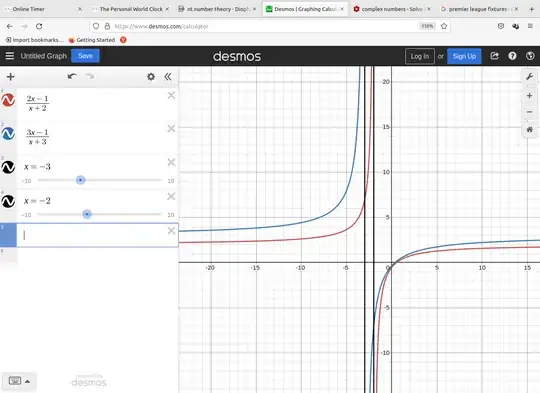
A possible way of doing this is to consider the cases $x<-3,-3<x<-2,x>-2$.
– Angae MT Sep 01 '24 at 18:13