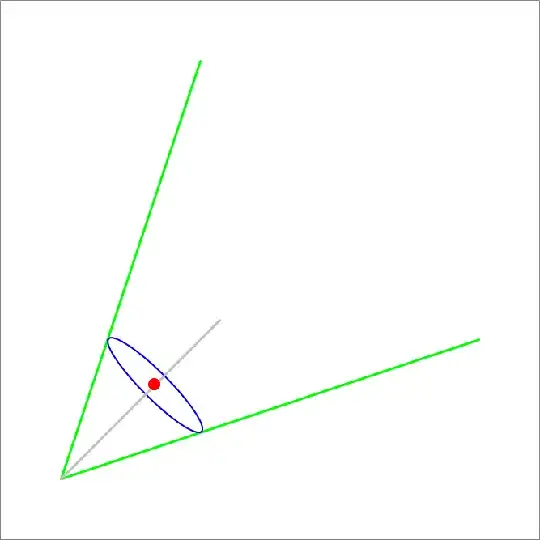
Given two lines, $\ell_1: y = 3 x - 2 $ and $\ell_2: y = \dfrac{1}{3} x + 6 $, and two points $P_1, P_2$ on lines $\ell_1$ and $\ell_2$ respectively, where $P_1 = (4, 10) $ and $P_2 = (6, 8) $, I want to find the equation of the line on which the center of all ellipses tangent to $\ell_1$ and $\ell_2$ at $P_1$ and $P_2$, respectively, lie.
What I've tried:
The equation of our ellipse is
$ (r - C)^T Q (r - C) = 1$
And the outward normal at a point $r_1$ is along the gradient of this quadratic function. That is,
$ k_1 g_1= Q (r_1 - C)$
For some $k_1$.
At $P_1$, the outward normal is
$ g_1 = \begin{bmatrix} -3 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $
And at $P_2$, the outward normal is
$ g_2 = \begin{bmatrix} \dfrac{1}{3} \\ -1 \end{bmatrix} $
Therefore,
$P_1 - C = k_1 Q^{-1} g_1 \hspace{10pt} (*)$
$P_2 - C = k_2 Q^{-1} g_2 $
I don't know how to proceed from this point.