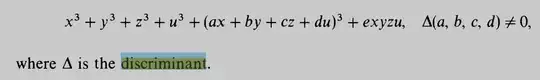I have good news & bad news.
The good news is that there is a method to get the Discriminant.
The bad news is that the eventual expression is going to be impractical & very hard to write out. We might have to use math Software.
(ACTION A) I would suggest you to check the earlier sections of that text to Explain/Define what a "Discriminant" is , according to Arnold et al.
(ACTION B) In case there is no mention of such Definitions , you can check this :
"Discriminants, Resultants and Multidimensional Determinants"
Authors : I.M. Gelfand , M.M. Kapranov , A.V. Zelevinsky
Publisher : Birkhauser Boston 1994
There it is given that Discriminant is a Polynomial in the co-efficients of $V(x_0,x_1,\cdots,x_n)$ where all the Partial Derivatives vanish.
In your Case , it gives :
$\partial V / \partial x = 0$
$\partial V / \partial y = 0$
$\partial V / \partial z = 0$
$\partial V / \partial u = 0$
$V=0$
Hence , we have :
$3x^2+3a(ax+by+cx+dz)^2+eyzu=0$
$3y^2+3b(ax+by+cx+dz)^2+exzu=0$
$3z^2+3c(ax+by+cx+dz)^2+exyu=0$
$3u^2+3d(ax+by+cx+dz)^2+exyz=0$
$x^3+y^3+z^3+u^3+(ax+by+cx+dz)^3+exyzu=0$
Solving this for $x,y,z,u$ , we will get some expression in terms of $a,b,c,d,e$ , which is the Discriminant here.
It will be highly cumbersome & impractical to even write it out here. Tools like Matlab / Maple / Mathematica / Macaulay can easily generate such Discriminant values automatically.
[[ Either Arnold text has a typo & it should have been $\Delta(a,b,c,d,e)$ or Authors have calculated it & checked that $e$ is unnecessary there ]]
(ACTION C) In Case that text is hard reading , I have this alternate reference , which is easy reading :
"Discriminants, resultants, and their tropicalization"
Course by Bernd Sturmfels - Notes by Silvia Adduci
Here Single variable Case is initially considered : when a function is $0$ & the Derivative is also $0$ , it implies multiple roots.
That Criteria easily gives us the Discriminants $\Delta (a,b,c)=b^2-4ac$ (Quadratic Case) & $\Delta (a,b,c,d)=27a^2d^2-18abcd+4ac^3+4b^3d-c^2d^2$ (Cubic Case)
Compare that with a Cubic Polynomial in 3 variables $x,y,z$ : According to Bernd & Silvia , it will 10 Co-efficients in Homogeneous Case & the Discriminant $\Delta$ will have 2040 terms!!!!
Hence , Arnold has not written out the Discriminant $\Delta$ when it is a function of 4 variables : it must have been a staggering expression , though automatic tools can easily compute that.
ADDENDUM :
I thought I might include a snippet from Gelfand et al Page 405 :

Here is Page 406 :

Naturally , Arnold has not given the Discriminant $\Delta$ expressions for most such cases !!!!