We want to find
$$I=\int_{-\pi}^\pi1+\lim_{n\to\infty}\min(\cos(x),\dots,\cos(nx))dx$$
Here is a picture of $1+\min(\cos(x),\dots,\cos(nx))$ for $n=50$:
$\displaystyle I_n= \int_{-\pi}^\pi1+\min(\cos(x),\dots,\cos(nx))dx$ has the following forms from software:
$$\begin{array}{r|c}I_1&2\pi\\\hline I_2&2\pi-3\sin\left(\frac\pi3\right)\\\hline I_3&2\pi-\frac13\left(9\sin\left(\frac\pi3\right)+5\sin\left(\frac\pi5\right)\right)\\\hline I_4&2\pi-\frac16\left(9\sin\left(\frac\pi3\right)+25\sin\left(\frac\pi5\right)+7\sin\left(\frac\pi7\right)\right)\\\hline I_5&2\pi-\frac1{30}\left(27\sin\left(\frac\pi3\right)+125\sin\left(\frac\pi5\right)+77\sin\left(\frac\pi7\right)+27\sin\left(\frac\pi9\right)\right)\\\hline I_6&2\pi-\frac1{30}\left(27\sin\left(\frac\pi3\right)+75\sin\left(\frac\pi5\right)+147\sin\left(\frac\pi7\right)+27 \sin\left(\frac\pi9\right)+22 \sin\left(\frac\pi{11}\right)\right)\end{array}\\\vdots$$
The denominators likely match A025555, the least common multiple of the first $n$ triangular numbers, so for $n>2$, we find:
$$I_n=2\pi-\frac2{\operatorname{LCM}(1,\dots,n)}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}a_{n,k}\sin\left(\frac\pi{2k+1}\right)$$
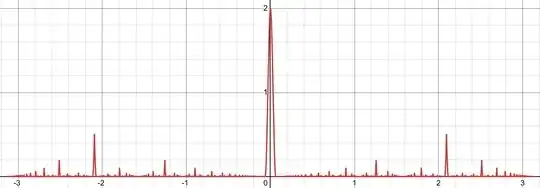
where the $a_{n,k}$ relates to A027446, “ Triangle read by rows: square of the lower triangular mean matrix”. Here is a graph showing the convergence as $n\to\infty$

$J=\int_{-\pi}^\pi1+\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}\min(\sin(x),\dots,\sin(nx))dx$ is also of interest. The fractals can be tested here. It seems that $\lim\limits _{n\to\infty}I_n=0$, but it is hard to tell.
How can one evaluate $I$, or maybe $J$?