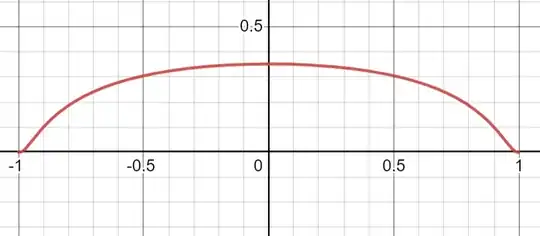
Expand using $\tan^{-1}$’s Maclaurin series and substitute $\frac1{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\to x$:
$$\int_{-1}^1 \tan^{-1}\left(\exp\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\right) \right) dx=2\sum_{n=0}^\infty\frac{(-1)^n}{2n+1}\int_1^\infty \frac{e^{-(2n+1)}}{x^2\sqrt{x^2-1}}dx$$
One apply @Metamorphy’s method in this answer, by using $\int_0^\infty e^{ax}da=\frac{e^x}x$ twice, and “generalized” Meijer G:
$$\int_1^\infty \frac{e^{-(2n+1)x}}{x^2\sqrt{x^2-1}}dx=\int_{2n+1}^\infty\int_b^\infty\int_1^\infty\frac{e^{-ax}}{\sqrt{x^2-1}}dx\,da\,db= \int_{2n+1}^\infty\int_b^\infty K_0(a)\,da\,db= \frac12\int_{2n+1}^\infty\int_b^\infty G_{0,2}^{2,0}\left(\frac a2,\frac12;0,0\right)\,da\,db$$
Now apply its integration formula to get
$$\int_1^\infty \frac{e^{-(2n+1)x}}{x^2\sqrt{x^2-1}}dx =2-(2n+1)\pi+G_{2,4}^{2,2}\left(\left(n+\frac12\right)^2;^{\ \ \ 1,\frac32}_{1,1,0,\frac12}\right)$$
after converting to the ordinary Meijer G function. Numerically, plugging in $\infty$ after integrating with respect to $b$ gives $2$. Therefore:
$$\boxed{\int_{-1}^1 \tan^{-1}\left(\exp\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\right) \right) dx=\frac{(2-\pi)\pi}4+\sum_{n=0}^\infty\frac{(-1)^n}{2n+1}\left(G_{2,4}^{2,2}\left(\left(n+\frac12\right)^2;^{\ \ \ 1,\frac32}_{1,1,0,\frac12}\right)-2\pi n\right)}$$
shown here:
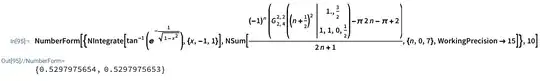
Unfortunately the Leibniz formula $\frac\pi4=\sum\limits_{n=0}^\infty\frac{(-1)^n}{2n+1}$ converges slowly, so everything must be in the sum to numerically test it. Also, if Wolfram Cloud calculates about $20+$ terms, numerical errors appear, so more working precision is needed. However, the sum quickly converges.