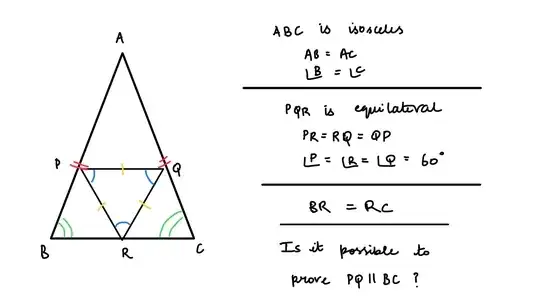
Triangle $ABC$ is isosceles. An equilateral triangle $PQR$ is inscribed in it with $R$ being the midpoint of $BC$. How can you prove $PQ \parallel BC$?

Triangle $ABC$ is isosceles. An equilateral triangle $PQR$ is inscribed in it with $R$ being the midpoint of $BC$. How can you prove $PQ \parallel BC$?
Please see the below diagram which gives a counter-example for obtuse angled isosceles triangle ($120$-$30$-$30$) as mentioned by John Omielan.
For $\angle BRP = 60^\circ + x, \angle CRQ = 60^\circ - x$ or vice versa with $0 \lt x \lt 30^\circ$ will give us points $P$ and $Q$ on sides $AB$ and $AC$ such that $\triangle PQR$ is equilateral but $PQ$ is not parallel to $BC$.
By law of sines, we can show that $120$-$30$-$30$ is the only isosceles triangle for which $PQ$ is not necessarily parallel to $BC$.
Say $\angle B = \angle C = y$ and $\angle BRP = 60^\circ + x, \angle CRQ = 60^\circ - x$
By law of sines in $\triangle BPR$,
$ \displaystyle \frac{\sin (180^\circ - (60^\circ + x+y))}{BR} = \frac{\sin y}{PR} \tag1$
By law of sines in $\triangle CQR$,
$ \displaystyle \frac{\sin (180^\circ - (60^\circ - x + y))}{CR} = \frac{\sin y}{QR} \tag2$
As $BR = CR$ and $PR = QR$, from $(1)$ and $(2)$ we obtain
$\sin (60^\circ - x + y) = \sin (60^\circ + x + y)$
So we either have $60^\circ - x + y = 60^\circ + x + y ~$ i.e. $ ~x = 0$. That leads to $\angle BRP = \angle CRQ = 60^\circ ~$ and $ ~PQ \parallel BC$.
Or we have,
$(60^\circ - x + y) + (60^\circ + x + y) = 180^\circ \implies y = 30^\circ$ and $\triangle ABC$ is $120$-$30$-$30$ triangle. In this case, it is not necessary that $ \angle BRP = \angle CRQ$. I have demonstrated this case in the first part of my answer.