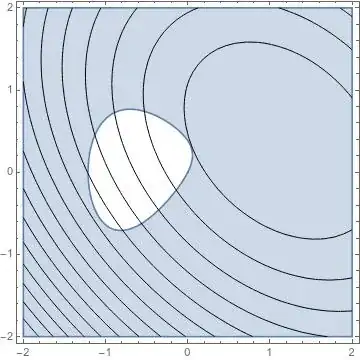
I'm trying to find an estimate for the region of attraction of an equilibrium point. The notes from Nonlinear Control by Khalil suggest that defining $$ V(x) = x^TPx, $$ where $P$ is the solution of $$ PA+A^TP=-I, $$ will yield the best results for an estimate. It also assures that the estimate can be found from these types of Lyapunov functions for exponentially stable equilibrium points.
The system I am studying is defined by $$ \begin{gathered} \dot{x}_1 = x_1 - x_1^3 + x_2 \\ \dot{x}_2 = x_1 - 3x_2. \end{gathered} $$ The linealization matrix around the equilibrium point $x^* = \{\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}},\frac{2}{3\sqrt{3}}\}$, is $A = \begin{bmatrix} -3 & 1 \\ 1 & -3\\ \end{bmatrix} $, and so, $P = \begin{bmatrix} 3/16 & 1/16 \\ 1/16 & 3/16\\ \end{bmatrix} $.
Given the previous values, I took the derivative of V(x) w.r.t. time and substituted the system in the equation (did it in Mathematica to try and simplify it as much as possible), giving $$ \dot{V}(x) = \frac{1}{8}\left(4x_1^2-3x_1^4+4x_1x_2-x_1^3x_2-8x_2^2\right). $$ Now I need to find a region where $\dot{V}(x)$ is negative definite, but when I try to use inequalities with the norm of $x$ I get only positive norms raised to a power, and so $\dot{V}(x)$ can never be negative definite.
Using $$ |x_1|\leq||x||, \quad |x_1x_2|\leq\frac{1}{2}||x||^2, $$ I arrived at $$ \begin{gathered} \dot{V}(x) \leq \frac{1}{8}\left(4||x||^2+3||x||^4+2||x||^2+\frac{1}{2}||x||^4+8||x||^2\right) \\ \leq \frac{1}{8}\left(14||x||^2+\frac{7}{2}||x||^4\right). \end{gathered} $$ As you can see, it never is negative.
Am I being overly aggresive with converting everything to norms? How can I find the region where $\dot{V}(x)$ is negative?
Thanks in advance.