If X is a continuous random variable which takes non-negative value, prove that the expectation of X can be calculated using the following integral:
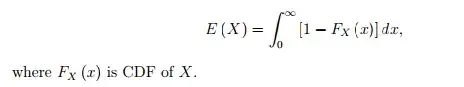
If X is a continuous random variable which takes non-negative value, prove that the expectation of X can be calculated using the following integral:
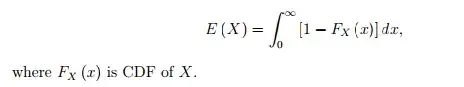
Write $x = \int_{[0,x)} 1\,dt$, so that $$ \eqalign{ E(X) &=E\left(\int_{[0,X)} 1\,dt\right) =E\left(\int_0^\infty{\Bbb 1}_{\{X>t\}} \,dt\right)\cr &= \int_0^\infty P(X>t) \,dt=\int_0^\infty [1-F_X(t)]\,dt.\cr } $$ (The third equality results from the Fubini/Tonelli theorem.) This argument works for any non-negative random variable, continuous or not.