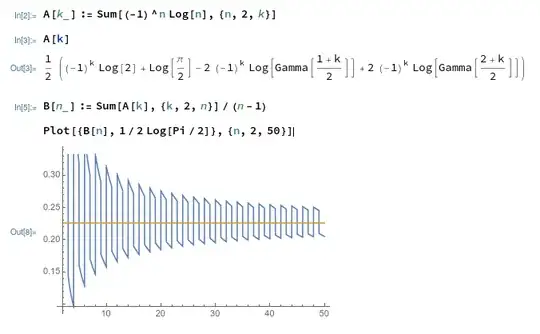
I accidentally stumbled on the following regularization of this divergent series:
$$\sum_{n=2}^\infty (-1)^n \log n "=" \frac{1}{2} \log \frac{\pi}{2}$$
I'm not familiar enough with regularization, so I wanted to ask if this result agrees with any other known regularization method?
I derived this result in the following way:
$$\log n=\int_0^\infty \frac{dx}{x} (e^{-x}-e^{-n x})$$
Now consider the function:
$$\sum_{n=2}^\infty (-1)^n (\log n) s^n=\int_0^\infty \frac{dx}{x} \left(e^{-x} \frac{s^2}{1+s}-\frac{s^2 e^{-2 x}}{1+s e^{-x}} \right)$$
$$\sum_{n=2}^\infty (-1)^n (\log n) s^n= \frac{s^2}{1+s}\int_0^\infty \frac{e^{-x}dx}{x} \frac{e^x-1}{e^x+s} $$
The right hand side converges for any $s>0$, and in particular, for $s=1$ we have:
$$\frac{1}{2}\int_0^\infty \frac{e^{-x}dx}{x} \frac{e^x-1}{e^x+1}=\frac{1}{2} \log \frac{\pi}{2}$$
I got the result with Wolfram Alpha, but I'm sure there's a proof somewhere on this site.
There's an interesting corollary here. If we write:
$$\sum_{n=2}^\infty (-1)^n (\log n) s^{n-1}= \frac{s}{1+s}\int_0^\infty \frac{e^{-x}dx}{x} \frac{e^x-1}{e^x+s} $$
And then integrate w.r.t. $s$ from $0$ to $1$, we obtain:
$$\sum_{n=2}^\infty (-1)^n \frac{\log n}{n}= \int_0^\infty \frac{\log(1+e^{-x})-e^{-x} \log 2}{x} dx= \gamma \log 2- \frac{\log^2 2}{2}$$