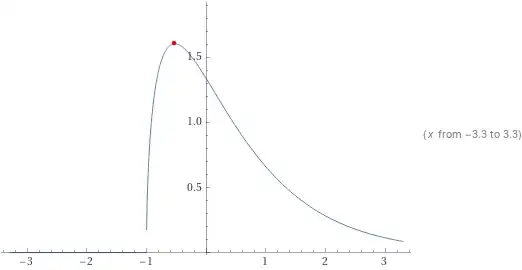
Define the reals $x,y$ as
$$ y = \max \Im ( W ( - \exp(x)) \exp(-x) ) $$
$W$ is the standard Lambert $W$ function and $\Im$ is the imaginary part.
How do we find $x$ and $y$?
Closed forms (allowing integrals, sums, etc), contour integrals, numerical methods?
I know how to express the local COMPLEX max on the complex plane for an analytic function by a contour integral.
I also know the Cauchy-Riemann equations that relate an analytic function's real and imaginary parts by differential equations.
Yet, this does not appear to help me. Maybe it should help me, but I do not know how.
I ask here for a case of the $W$ function, because i do not want to ask too General questions. But I am also interested in general methods of course.