I was solving a uniform probability distribution question, the question was : $\\$ probability of meeting two people A and B between 1 PM and 2 PM, if none of them waits more than 15 minutes for the other. Given that probability of arrival is uniform between 1 PM to 2 PM for both of them.
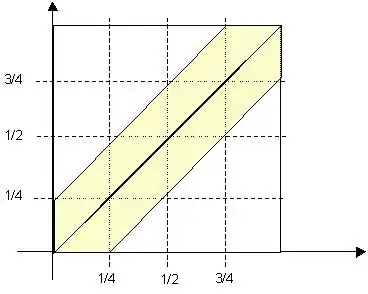
I took the time span as L and separated two zones. [0,3L/4] and [3L/4,L].
In the first zone if A comes first at time x B has the option to come anytime in [x,x+L/4]. In the second zone,if A comes first at x then B must come in [x,L-x].
I did the integration in two zones and found P(A-B) = 7/32,and multiplied by 2 gives the total probability.
Later I framed (visualized) the same question as follows : In Cartesian co-ordinate system,along the x axis two points p and q are selected uniformly at random in $\left [ 0,L \right ]$ where L > 0.What is the probability of $\text{dist(p,q)} \leq \frac{L}{4}$.
Then I modified it to two dimensional geometry problem :
In the Cartesian plane, selection of a point P along the y axis in [0,2] is uniformly random. Similarly selection of a point Q along the x axis in [0,2] also uniformly distributed. What is the probability of the area of the triangle POQ to be less than or equal to 1, where O is the origin ?
I solved it using integration in two parts:
- if x is in [0,1] then y is allowed to have the full range of [0,2]
- if x is in [1,2] then y is allowed to have the range [0,2/x]
I got probability as 0.846.
My questions are:
- Is it correct ?
- What is the more generic way to to such problem ? In both the above cases I drew some geometry and did some integration. In the second problem, we are interested in the quantity area (xy/2). But what if we are given a random expression like (3xy+x^2). Please elaborate any other method.