This answer is based on the study Empirical evidence on the link between object-oriented measures and external quality attributes: a systematic literature review (PDF) by Ronald Jabangwe, Juurgen Borstler, Darja Smite, Claes Wohlin, 2014. They selected 99 papers to review in total.
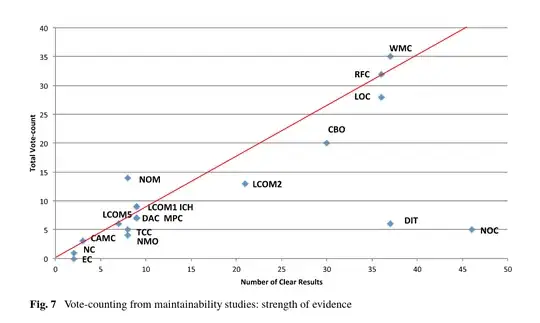
"Vote counting" here means to get a point (or two) for each study that shows a strong connection between the specific metric and maintainability.
Description of important metrics
WMC = Weighted method for classes.
Weighted methods for Class (WMC) was originally proposed by C&K as the sum of all the complexities of the methods in the class 3.
LOC = Lines of code; todo: size of class, function, library, code-base?
RFC = Response for class
This is the size of the Response set of a class. The Response set for a class is defined by C&K as 'a set of methods that can potentially be executed in response to a message received by an object of that class' 3.
CBO = Coupling between objects
Coupling between objects (CBO) is a count of the number of classes that are coupled to a particular class i.e. where the methods of one class call the methods or access the variables of the other 3.
DIT = Depth of inheritance tree
Depth of Inheritance Tree (DIT) is a count of the classes that a particular class inherits from 3.
NOC = Number of children
Number of Children (NOC) is defined by C&K the number of immediate subclasses of a class 3.
Quotes from the study
There are insufficient numbers of studies on maintainability to draw conclusions. Nevertheless, Fig. 7 [picture above] shows that there is a potential link between maintainability, and measures that quantify complexity and cohesion properties.
Results from our systematic review suggest that inheritance measures have a weak link with reliability and maintainability across studies, particularly the two inheritance measures DIT and NOC.
The study also notes that code metrics must be regarded in an organizational context:
team structure and team strategy can vary across development settings, and studies show that such organizational characteristics have an impact on quality
