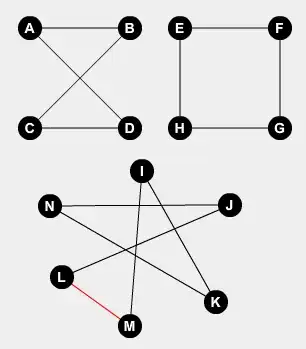
A further result has been added below:
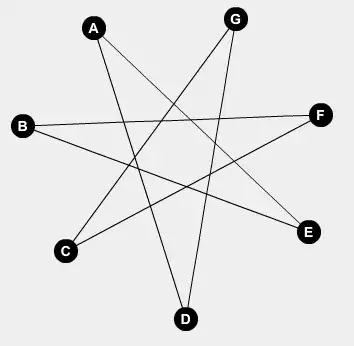
You may want to require that distinct edges intersect in at at most one point. Without this additional assumption, even cycles can be drawn in the way you describe. (Take your A-B-C-D graph and move A and B to the edge CD, with A closer to C.)
With this extra requirement, you definitely can’t draw an even cycle.
Suppose to the contrary, and let the cycle be $v_1v_2\cdots v_{2k} v_1$. Edges $v_1v_2$ and $v_3v_4$ cross, and with the extra requirement, $v_1$, $v_2$, and $v_3$ can’t be collinear (assuming coincident vertices are also disallowed). WLOG, assume the edge $v_1v_2$ is horizontal and $v_3$ is above the line through $v_1$ and $v_2$. Then $v_4$ is necessarily below that line, $v_5$ is above, and so on. But then $v_{2k}$ and $v_3$ are on opposite sides of that line, so $v_2v_3$ and $v_{2k}v_1$ are disjoint.
Added, based on discrete’s addition to the question:
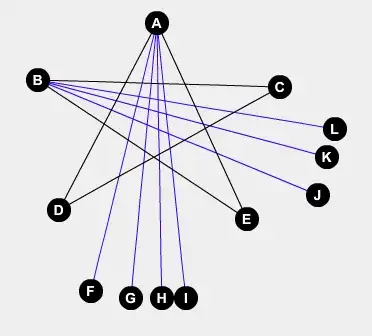
Let $G$ be a graph that can be drawn without disjoint edges. Then no vertex of $G$ can have 3 neighbors, each of which has degree at least 2.
Proof: Suppose $G$ is drawn without disjoint edges, and $v$ is adjacent to $a$, $b$, and $c$, each of degree at least $2$. We will obtain a contradiction.
[Idea of proof: The three edges $av$, $bv$, and $cv$ must all lie in one half-plane with $v$ on its boundary, and the “middle” vertex cannot have another edge that intersects the other two, as required.]
Consider the half-planes of $\mathbb{R}^2$ that are on the two sides of the line through $a$ and $v$. Except for $av$, any edge incident on $a$ or $v$ lies entirely within just one of these half-planes (the one containing its vertex that isn’t $a$ or $v$). In particular, edges $vb$ and $vc$ each lie within one of these half-planes, and so does the edge from vertex $a$ that is not the edge $av$. The latter edge must intersect both $ab$ and $ac$, so $b$ and $c$ must be in the same half-plane with respect to $av$. Similarly, $a$ and $c$ must be in the same half-plane with respect to $bv$, and $a$ and $b$ must be in the same half-plane with respect to $cv$. This is impossible. If $b$ and $c$ are in the same half-plane with respect to $av$, then either $0<\angle avb < \angle avc \le \pi$ or $0<\angle avc < \angle avb \le \pi$, and the “middle” edge of the larger angle leaves one vertex in each of the half-planes it creates.