The polar coordinates of an ellipse drawn from one of the focci is
$$ r(\theta) = \frac{a\, (1-\epsilon^2)}{1+\epsilon\,\cos \theta} $$
where $a$ is the semi-major axis, $b$ the semi-minor axus and $\epsilon = \sqrt{1-(b/a)^2}$ is the eccentricity.
To rotate the ellipse, add a phase to the angle $\theta$.
To draw a segment, limit $\theta$ to something less than $\theta = 0 \ldots 2\pi$.
To draw points, just enter the angle values you want points for.
I have made an example C# WinForms Gist that uses the built-in System.Numerics.Vector2 objects to define the geometry of objects. File Geometry.cs contains the routines that defined the points on the ellipse. File Gdi.cs contains the extension methods to draw various things on a System.Drawing.Graphics object, but using Vector2 for model-based coordinates instead of PointF pixel-based coordinates. Objects are drawn from the center of the form, and with some specified scale to convert between model coordinates and pixels.
The visual result is:
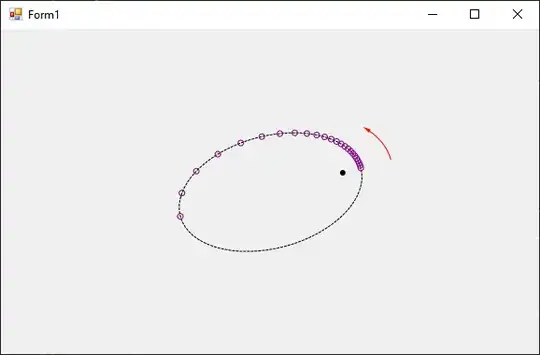
The code that draws the ellipse, the arrow and the points calls a function GetPointsOnEllipseArc() to produce the points on the ellipse.
Care must be taken because all drawing routines in Gdi.cs accept angles in degrees, and the geometry routines in Geometry.cs accept angles in radians.
Here is the drawing code inside the form
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)
{
base.OnPaint(e);
e.Graphics.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias;
e.Graphics.TranslateTransform(ClientSize.Width / 2, ClientSize.Height / 2);
float scale = 20;
Gdi.Stroke.Color = Color.Black;
Gdi.Stroke.DashStyle = DashStyle.Dash;
Vector2 center = Vector2.Zero;
float semiMajor = 5f, semiMinor = 3f;
float tiltAngle = 15;
e.Graphics.DrawEllipse(scale, center, semiMajor, semiMinor, tiltAngle);
Gdi.Stroke.DashStyle = DashStyle.Solid;
Gdi.Stroke.AddEndArrow(4f);
Gdi.Stroke.Color = Color.Red;
float factor = 4 / 3f;
e.Graphics.DrawEllipseArc(scale, center, factor*semiMajor, factor*semiMinor, 0, 20, tiltAngle);
Gdi.Stroke.RemoveEndArrow();
float focusDistance = (float)Math.Sqrt(semiMajor * semiMajor - semiMinor * semiMinor);
Vector2 focus = center + new Vector2(focusDistance * (float)Math.Cos(tiltAngle*Geometry.deg), focusDistance * (float)Math.Sin(tiltAngle*Geometry.deg));
Gdi.Fill.Color = Color.Black;
e.Graphics.FillPoint(scale, focus);
Gdi.Stroke.Color = Color.Purple;
var points = Geometry.GetPointsOnEllipseArc(focus, semiMajor, semiMinor, 24, 0, 180 * Geometry.deg, tiltAngle * Geometry.deg);
foreach (var point in points)
{
e.Graphics.DrawPoint(scale, point);
}
}
Notice the manual calculation of the focus point, and the calling of Geometry.GetPointsOnEllipseArc() to return the list of points on the ellipse. This uses the polar equation shown above.
/// <summary>
/// Gets points on an ellipse arc (partial ellipse).
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// The points are drawn from the focus of the ellipse and are spaced
/// by equal angles in polar coordinates.
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="focus">The focus point of the ellipse.</param>
/// <param name="semiMajor">The semi-major axis.</param>
/// <param name="semiMinor">The semi-minor axis.</param>
/// <param name="numPoints">The number points.</param>
/// <param name="azimuthOffset">The azimuth offset angle in radians, CCW.</param>
/// <param name="azimuthSweep">The azimuth sweep angle in radians, CCW.</param>
/// <param name="tiltAngle">The tilt angle in radians, CCW from horizontal.</param>
/// <returns>An array of <see cref="Vector2"/> points.</returns>
static public Vector2[] GetPointsOnEllipseArc(Vector2 focus, float semiMajor, float semiMinor, int numPoints, float azimuthOffset, float azimuthSweep, float tiltAngle = 0)
{
float e = (float)Math.Sqrt(1 - (semiMinor / semiMajor) * (semiMinor / semiMajor));
float Δθ = azimuthSweep / (numPoints - 1);
float ct = (float)Math.Cos(tiltAngle), st = (float)Math.Sin(tiltAngle);
Vector2[] points = new Vector2[numPoints];
for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; i++)
{
// get azimuth angle along the ellipse
float θ = azimuthOffset + i * Δθ;
// get polar coordinate of ellipse r(θ)
float r = semiMajor * (1 - e * e) /(float)(1 + e * Math.Cos(θ));
// get axis aligned (x,y) point from foci
float x = r * (float)Math.Cos(θ), y = r * (float)Math.Sin(θ);
// get rotated (x,y) point
Vector2 localPoint = new Vector2(ct * x - st * y, st * x + ct * y);
points[i] = focus + localPoint;
}
return points;
}

gist. There is a bug in the code, lines 33 and 34. It is a common mistake I have seen when rotating vectors. – John Alexiou Apr 26 '23 at 11:41GEOMETRY.F90I found this Fortran code that splits a tilted ellipse into points. You have toCtrl-Fthe source file forELLIPSE_POINTS_2Dto find it. – John Alexiou May 17 '23 at 13:54