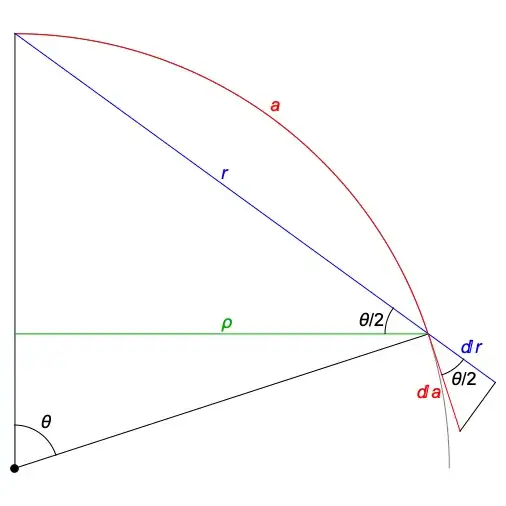
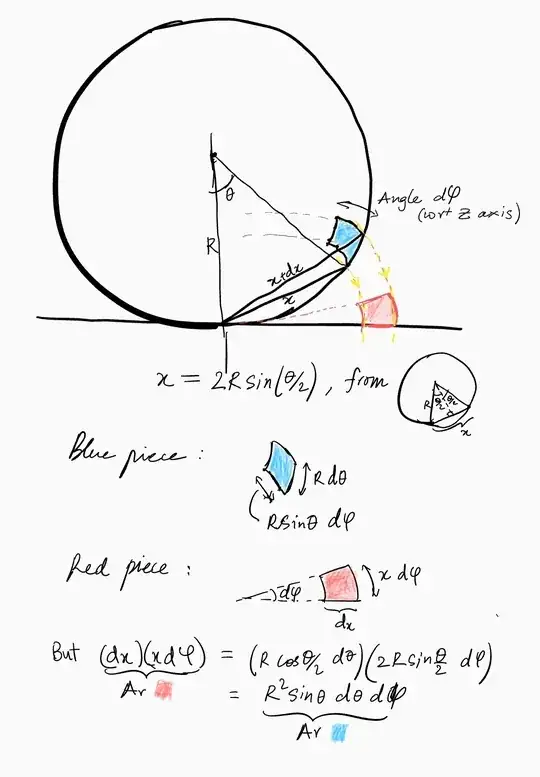
(If you're surprised by the title — $r$ is not what you (perhaps) think it is : )
Let $x$ be a point on a sphere $S$ and let $U$ be some sphere with center $x$ that intersects $S$.
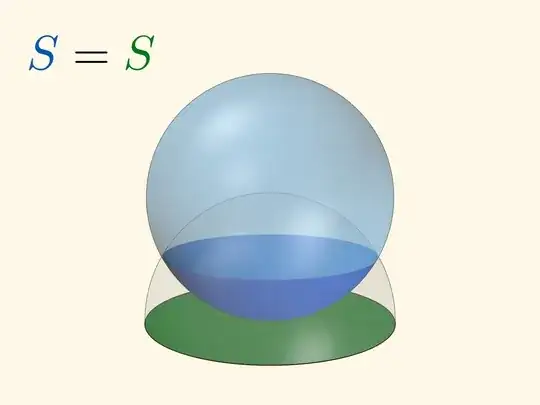
Claim¹. The spherical cap cut out from $S$ and the circle cut out from $T_xS$ (tangent plane to $S$ at $x$) have the same area.
In other words, the area of a spherical cap is $\pi r^2$ where $r$ is the distance from its center $x$ to its boundary. (So we have a very simple formula for circle area in spherical geometry. But it's somewhat strange: $r$ is neither spherical nor Euclidean radius of the circle!)
Question. How to prove this geometrically?
It can be proved by direct computation² but surely there should be… some explanation why this map from a sphere to a plane is area-preserving, perhaps?
One interesting special case is $r=2R$ (where $R$ is the radius of $S$). The 'cap' in this case is the whole sphere — and $\pi r^2=4\pi R^2$. So a (good) answer to my question would give (yet another) explanation of sphere's surface area formula.
¹ I learned this from A. Akopyan.
² For example: the height of the cap is $r^2/2R$ (because $h/r=(r/2)/R$), so by Archimedes' hatbox lemma the area is $2\pi R\cdot r^2/2R=\pi r^2$.