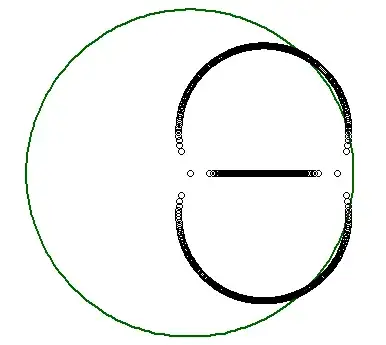
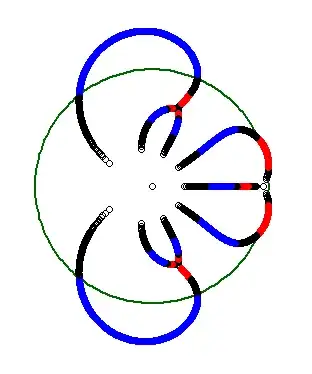
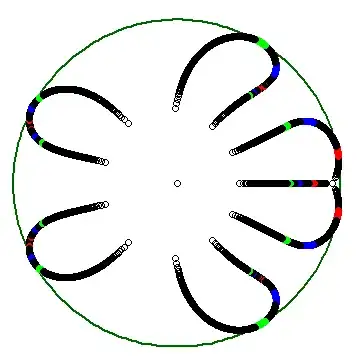
I think Cauchy's argument principle can provide an upper bound(possibly not tight). As is well-known, Cauchy's argument principle says that for a polynomial $p(z)$ which does not vanish on $|z|=1$, its number of roots counted with multiplicity in $|z|<1$ is given by the formula
$$
\frac{1}{2\pi i}\int_{|z|=1} \frac{p'(z)}{p(z)}dz.
$$ Let us denote $p_\alpha (z) = \pi(\alpha b)(z)$ for $\alpha \in\mathbb{R}$ and fixed $b\in\mathbb{R}^n$. We will use the integer-valued continuous function
$$
F:\alpha \mapsto \frac{1}{2\pi i}\int_{|z|=1} \frac{p_\alpha'(z)}{p_\alpha(z)}dz,
$$ defined for $\alpha$ such that $p_\alpha$ does not vanish on the unit circle. However, we can easily see that the number of such values of $\alpha$ is at most $n+1$.
Assume $p_\alpha(e^{-i\theta})= 0$ for some $\theta$. Then, $$
1+ \alpha(b_{n-1}e^{i\theta} +b_{n-2}e^{i2\theta} +\cdots +b_0e^{in\theta}) = 0\quad\cdots(*).
$$Then, in particular, $b_{n-1}e^{i\theta} +b_{n-2}e^{i2\theta} +\cdots +b_0e^{in\theta}$ is real-valued, and hence its imaginary part
$$
\sum_{k=1}^n b_{n-k}\sin(k\theta) = 0.
$$ If we denote $T_n$ by $n$-th Chebyshev polynomial, then it holds $\sin\theta\cdot T_n'(\cos\theta) = n\sin n\theta$. Here, $U_{n-1}:= \frac{1}{n}T_n'$ is a polynomial of degree $n-1$. From this, we may write
$$
\sin\theta\sum_{k=1}^n b_{n-k}U_{k-1}(\cos\theta) =\sin\theta \cdot P(\cos\theta)= 0,
$$ where $P = \sum_{k=1}^n b_{n-k}U_{k-1}$ is a polynomial of degree at most $n-1$. Thus, solving the above equation, we get $\theta = 0\text{ or }\pi$, or $\cos\theta= v_1, v_2,\ldots v_{n-1}$, where each $v_i$ is a root of $P=0$.
Now, from $(*)$, we have
$$
1+ \alpha(b_{n-1}\cos\theta +b_{n-2}\cos2\theta +\cdots +b_0\cos n\theta) = 0,
$$ and the number of possible values of $\alpha$ is at most $n+1$. Let these values $-\infty =:\alpha_0 <\alpha_1<\alpha_2< \ldots< \alpha_N<\alpha_{N+1}:=\infty$. Then, $F$ is well-defined on each $(\alpha_j, \alpha_{j+1})$ and is a continuous, integer-valued function. Thus, $F \equiv m_j$ on each $(\alpha_j, \alpha_{j+1})$. Our next goal is to investigate how the component of $L\cap \Delta$ looks like using the information of $F$.
(i) Notice that $\alpha_j \neq 0$ for all $j$ and there is unique $j'$ such that $0\in (\alpha_{j'}, \alpha_{j'+1})$. Clearly, on $(\alpha_{j'}, \alpha_{j'+1})$, $F$ is identically $n$.
(ii) On the other hand, note that $\lim_{|\alpha|\to\infty} F(\alpha) \leq n-1$ since as $|\alpha| \to \infty$, the roots of $p_\alpha$ acts like that of $n-1$-degree polynomial.
(iii) If $F = n$ on adjacent intervals $(\alpha_j, \alpha_{j+1})$ and $(\alpha_{j+1}, \alpha_{j+2})$, then we can conclude that on $\alpha = \alpha_{j+1}$, $p_\alpha$ has all its roots on the "closed" unit disk, since on a punctured neighborhood of $\alpha_{j+1}$, all the roots are contained in the open unit disk, hence in the closed one.(Note that the behavior of zero set is continuous.) Thus we conclude in this case, $(\alpha_j, \alpha_{j+1})$ and $(\alpha_{j+1}, \alpha_{j+2})$ are contained in the same component (together with $\alpha_{j+1}$).
(iv)There is possibility that all the roots of $p_{\alpha_{j+1}}$ are contained in the closed unit disk (and of course some of them are on the boundary), even though $F<n$ on $(\alpha_j, \alpha_{j+1})$ and $(\alpha_{j+1}, \alpha_{j+2}).$ In this case the singleton set $\{\alpha_{j+1}\}$ forms a component.
Summing this up, we can see that the components of $L\cap \Delta$ is of the form $(\alpha_i, \alpha_{j})$, $[\alpha_i, \alpha_{j})$, $(\alpha_i, \alpha_{j}]$, or $[\alpha_i, \alpha_{j}]$ for some $i\leq j$ (if equal, then it becomes sigleton set). And by (iii), $(\alpha_i, \alpha_{j})$ and $(\alpha_j, \alpha_{k})$ cannot be separated, and one of its component should include non-singleton component containing $0$. From this, the number of components can be greatest when all the components are of the form $\{\alpha_j\}$ except for one $(\alpha_{j'},\alpha_{j'+1})$. Hence we conclude that the number $k$ of components satisfy
$$k \leq N-1 \leq n.$$
$\textbf{EDIT:}$ The above argument is valid if it were that
$$\Delta = \{ x\in \mathbb R^n: \pi(x) \text{ has roots in the }\textbf{closed} \text{ unit disk of } \mathbb C\}.$$ There was a slight revision after I wrote. However, the argument can be easily modified to give the same bound $k\leq n$ for the case
$$\Delta = \{ x\in \mathbb R^n: \pi(x) \text{ has roots in the open unit disk of } \mathbb C\}.
$$
$\textbf{EDIT:}$ I've thought about when it happens that some paths of roots touch the boundary and get back to the interior. As a result, I could reduce the previous bound $n$ to $\frac{n+1}{2}$.
Assume that on $F=n$ on $(\alpha_{j-1}, \alpha_{j})\cup (\alpha_{j}, \alpha_{j+1}).$ By definition, $p_{\alpha_j}(z^*)=0$ for some $|z^*|=1$. The first claim is that the multiplicity of $z^*$ is $1$. Here is heuristic argument. Assume $z^*$ has multiplicity $L$. Then, we have for $q(z) = b_{n-1}z^{n-1} + b_{n-2}z^{n-2} + \cdot + b_0$,
$$
p_\alpha(z) = p_{\alpha_j}(z) + (\alpha-\alpha_j)q(z) = (z-z^*)^L r(z) + (\alpha-\alpha_j)q(z),
$$ where $r(z)$ is a polynomial s.t. $r(z^*) \neq 0$. As $\alpha \sim \alpha_j$, we have $z \sim z^*$, and solving $p_\alpha = 0$ is asymptotically equivalent to
$$
(z-z^*)^L \sim - (\alpha-\alpha_j)\frac{q(z^*)}{r(z^*)}.
$$Note that $q(z^*) \neq 0$ since if $q(z^*) = 0$, then $p_{\alpha_j}(z^*) = 0$ implies $z^* = 0$, leading to contradiction. Let $\zeta_L$ be $L$-th root of unity and $\omega^{\frac{1}{L}}$ denote one of the ($L$)-solutions of $z^L= \omega$. This shows
$$
\lambda_k(\alpha) \sim z^* + \left(- (\alpha-\alpha_j)\frac{q(z^*)}{r(z^*)}\right)^{\frac{1}{L}}\zeta^k_L, \quad k=1,2,\ldots, L,
$$are asymptotic roots of $p_\alpha (z) = 0$. We will see that as $\alpha \uparrow \alpha_j$ or $\alpha \downarrow \alpha_j$, it is impossible that all the $\lambda_k(\alpha)$ lie in the open unit disk.
Formal proof of this claim asserting that an analytic function that has $L$-th zero behaves locally like $L$-to-$1$ function requires a version of Rouche's theorem and argument principle. Assume an analytic function $f$ has zero of $L$-th order at $z=0$. For sufficiently small $\epsilon$, $f$ does not vanish on $0<|z| \leq \epsilon$, and
$$
\frac{1}{2\pi i}\int_{|z|=\epsilon} \frac{f'(z)}{f(z)}dz = L
$$ gives the number of zeros on $|z|<\epsilon$. If we perturb $f$ by $\eta \cdot g(z)$ as $\eta \to 0$, then
$$
\frac{1}{2\pi i}\int_{|z|=\epsilon} \frac{f'(z)+\eta g'(z)}{f(z)+\eta g(z)}dz = L
$$ for $|\eta| < \frac{\min_{|z|=\epsilon}|f(z)|}{\max_{|z|=\epsilon}|g(z)|}$.(This is by Rouche's theorem.) Thus, small perturbation does not affect the number of zeros on a neighborhood of $0$.
Let us consider the equation
$$
z^Lf(z) = u^L\quad\cdots (***),
$$where $f$ is analytic, $f(0) = 1$ and $u\in\mathbb{C}$ is an $\mathcal{o}(1)$ quantity (this means $|u|\to 0$.) If $f = 1$, then the exact roots of the equation is
$$
\lambda_k = u\zeta^k,\quad k=1,2,\ldots, L,
$$where $\zeta$ is the $L$-th root of unity. Our claim about asymptotic roots of $(***)$ is that
$$
\lambda_k(u) = u(\zeta^k + \mathcal{o}_u(1)),\quad k=1,2,\ldots, L,
$$ is the roots of $(***)$. Here, $\mathcal{o}_u(1)$ denotes some quantity going to $0$ as $|u|\to 0$. Proof is simple. Modify the equation $(***)$ to
$$
z^L f(uz) = 1.
$$ Then $u\lambda'_k, k=1,2,\ldots, L$ is the roots of $(***)$ where $\lambda'_k$ denotes roots of modified equation. But as $|u|\to 0$, the modified equation converges to $z^L = 1$ whose exact roots are $\zeta^k, k=1,2,\ldots, L.$ By Rouche's theorem, each $\lambda'_k$ should be located in a neighborhood of $\zeta^k$. This proves the claim.
Actually this implies a seemingly stronger assertion that if
$$
z^Lf(z) = v^L
$$ where $v = u(1+ \mathcal{0}_u(1))$, then
$$
\lambda_k = u(\zeta^k + \mathcal{o}_u(1)).
$$ And we will use this version. We are assuming that
$$
(z-z^*)^L \frac{r(z)}{r(z^*)} = -(\alpha-\alpha_j)\frac{q(z)}{r(z^*)}.
$$ As $\alpha \to \alpha_j$, the roots $z\to z^*$ by Rouche's theorem. Thus,
$$
-(\alpha-\alpha_j)\frac{q(z)}{r(z^*)} = -(\alpha-\alpha_j)\left(\frac{q(z^*)}{r(z^*)}+\mathcal{o}_{\alpha-\alpha_j}(1)\right).
$$ By the above claim, we get
$$
\lambda_k(\alpha) = z^* + \left(- (\alpha-\alpha_j)\frac{q(z^*)}{r(z^*)}\right)^{\frac{1}{L}}(\zeta^k + \mathcal{o}_{\alpha-\alpha_j}(1))
$$ as claimed.
We can see that if $L\geq 2$, then $\lambda_k, k=1,2,\ldots, L$ comes from $L$ different directions and they are equally spaced. If $L\geq 3$, we can easily see that it is impossible for all the $\lambda_k$ to lie in the unit circle. The case $L=2$ is more subtle, but we can see that it is also impossible in this case. (By noting that the unit circle has a positive curvature at each point.) Hence, $L$ should be $1$. We now know that $z^*$ should have multiplicity $1$, and
$$
\lambda(\alpha) = z^* -(\alpha-\alpha_j)\left(\frac{q(z^*)}{r(z^*)} +\mathcal{o}_{\alpha-\alpha_j}(1)\right).
$$ We see that $r(z^*) = p'_{\alpha_j}(z^*)$ by definition, and $\frac{\partial}{\partial \alpha}\lambda(\alpha_j) = - \frac{q(z^*)}{p'_{\alpha_j}(z^*)}$. For $\lambda(\alpha)$ to get back to the inside, it must be that
$$
\frac{q(z^*)}{p'_{\alpha_j}(z^*)} = -\frac{\partial}{\partial \alpha}\lambda(\alpha_j) = i\beta z^*
$$ for some real $\beta$ (that is, tangent vector should be orthogonal to the normal vector $z^*$.) From now on, let us write $\alpha_j$ as $\alpha^*$ for notational convenience.
Hence, we have $q(z^*) = i\beta z^* p_{\alpha^*}'(z^*) $. From $p_{\alpha^*}(z^*) = 0$, we also have
$$(z^*)^n = -\alpha^* q(z^*) = -i\alpha^*\beta z^*p'_{\alpha^*}(z^*)=-i\alpha^*\beta z^*(n(z^*)^{n-1} + \alpha^*q'(z^*)).
$$
Hence, $(1+i\alpha^*\beta n)(z^*)^{n} = -i(\alpha^*)^2\beta z^*q'(z^*),$ and we get
$$
(z^*)^n = \frac{-i(\alpha^*)^2\beta}{1+i\alpha^*\beta n}z^*q'(z^*) = -\alpha^*q(z^*),
$$
$$
\frac{i\alpha^*\beta}{1+i\alpha^*\beta n}z^*q'(z^*) =q(z^*).
$$ Note that it holds that
$$
\frac{z^*q'(z^*)}{q(z^*)} = n -\frac{i}{\alpha^*\beta}.
$$(Note that $q(z^*) \neq 0 $ and $\beta \neq 0$.) If we take conjugate on both sides, since $q(z)$ is a real polynomial, we have
$$
\frac{\overline{z^*}q'(\overline{z^*})}{q(\overline{z^*})} = n +\frac{i}{\alpha^*\beta}.
$$ This means $z^*$ cannot be $\pm 1$.
To derive an equation about $z^*$, let us write $z^* = e^{-i\theta}$.
Then we have from $(z^*)^n= -\alpha^*q(z^*)$, that
$$
1 = -\alpha^*\left(\sum_{k=1}^{n} b_{n-k} e^{ik\theta}\right).
$$Also from $(z^*)^n = \frac{-i(\alpha^*)^2\beta}{1+i\alpha^*\beta n}z^*q'(z^*)$, we have
$$
\frac{1+i\alpha^*\beta n}{i\alpha^*\beta}=n - \frac{i}{\alpha^*\beta} = -\alpha^*\left(\sum_{k=1}^{n} (n-k)b_{n-k} e^{ik\theta}\right).
$$ Both equations together yields:
$$
1 = -\alpha^*\left(\sum_{k=1}^{n} b_{n-k} e^{ik\theta}\right),
$$
$$
\frac{i}{\alpha^*\beta} = -\alpha^*\left(\sum_{k=1}^{n} kb_{n-k} e^{ik\theta}\right).
$$ Take the imaginary part for the former and the real part for the latter. Then,
$$
\sum_{k=1}^{n} b_{n-k} \sin(k\theta)=\sin\theta\cdot P(\cos\theta) = 0,
$$
$$
\sum_{k=1}^{n} kb_{n-k} \cos(k\theta)=\cos\theta\cdot P(\cos\theta) -\sin^2\theta\cdot P'(\cos\theta)=0,
$$ where $P := \sum_{k=1}^n b_{n-k}U_{k-1}$ is a polynomial of degree at most $n-1$. We already know $\sin\theta \neq 0$ since $e^{i\theta}$ is not real. Thus, it must be that $P(\cos\theta) = P'(\cos\theta) = 0$, meaning that $P(v)$ has a multiple root at $v = \cos\theta\in (-1,1)$. Recall that the roots of $P(v)=0$ were used to prove that the number of possible $\alpha$'s is at most $n+1$. Each possible $\alpha$ was related to the root of the equation $\sin\theta \cdot P(\cos\theta) =0$ by
$$
\alpha = -\frac{1}{b_{n-1}\cos\theta + \cdots + b_0\cos n\theta}.
$$
Now, suppose $P(v)$ has roots $v_1,\ldots, v_k, w_1,\ldots, w_l$ in $(-1,1)$ where each $v_i$ has multiplicity $1$ and each $w_j$ is multiple roots. Then we must have $k + 2l \leq n-1.$ Some of $v_i$ and $w_j$ are mapped to $\alpha_i$ and $\beta_j$ via the above formula. Some may not because $b_{n-1}\cos\theta + \cdots + b_0\cos n\theta$ may vanish for $\cos\theta = v_i$ or $w_j$. Adding $-\frac{1}{b_{n-1} + \cdots + b_0}$ and $-\frac{1}{-b_{n-1} + \cdots + b_0(-1)^n}$ to the set of $\alpha_i$'s, we finally get $A = (\alpha_i)_{i\leq l'}, B=(\beta_j)_{j\leq k'}$ where $l' + 2k' \leq n+1$. We may assume that $A$ and $B$ are disjoint by discarding $\alpha_i$ such that $\alpha_i =\beta_j$ for some $j$. Order the set $A\cup B$ by $$\gamma_0=-\infty <\gamma_1 < \gamma_2 <\cdots< \gamma_{l'+k'} <\infty=\gamma_{l'+k'+1}.$$ If $\gamma_i\in A$, then on one of the $(\gamma_{i-1},\gamma_i)$ and $(\gamma_{i},\gamma_{i+1})$, $F$ should be $<n$. Let $R$ be the family of intervals $(\gamma_{i},\gamma_{i+1})$ on which $F<n$. It must include $(-\infty,\gamma_1)$ and $(\gamma_{l'+k'},\infty)$. And it follows that if $\gamma_i\in A$, then it must be one of the end points of some interval in $R$. This restricts the cardinality of $A$ by
$$
l' = |A|\leq 2 + 2(|R|-2)=2|R|-2.
$$ Note that $k'+l'+1-|R|$ is the number of intervals on which $F=n$. Thus, we have
$$
k'+l'+1-|R|\leq k' + l' +1 -\frac{l'+2}{2}=k'+\frac{l'}{2}\leq \frac{n+1}{2}.
$$, as we wanted.
To conclude, let us define the constant $C_n$ by $$
C_n = \max\{N\geq 1\;|\;\Delta\cap \{\alpha b\}_{\alpha\in\mathbb{R}}\text{ has }N\text{ components for some } b\in \mathbb{R}^n\}.
$$ Then, we have $$
C_n \leq \frac{n+1}{2}.$$
(Note: Especially, for $n=2$, we have $C_2 = 1$ and hence $\Delta\cap\{\alpha b\}_{\alpha \in \mathbb{R}}$ is connected for every $b \in \mathbb{R}^2$.)