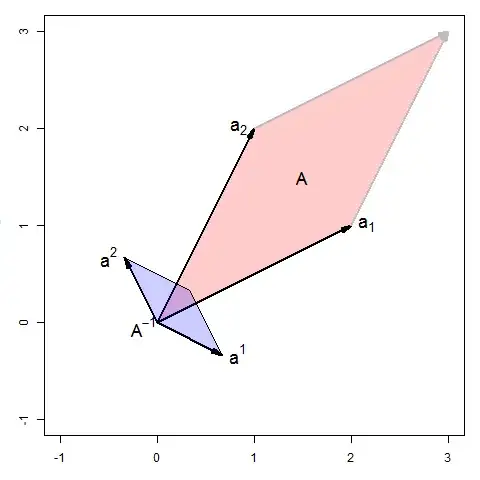
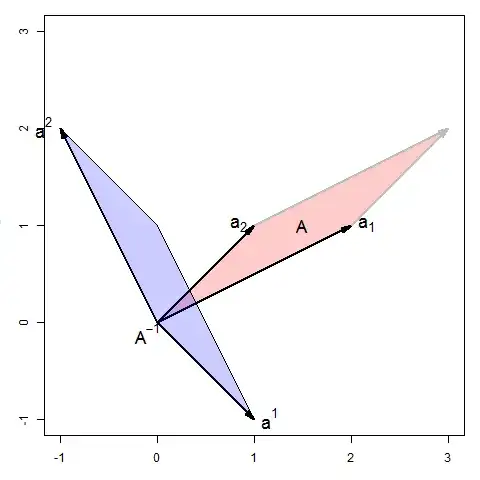
Let $A$ be an invertible $n \times n$ matrix. Suppose we interpret each row of $A$ as a point in $\mathbb{R}^n$; then these $n$ points define a unique hyperplane in $\mathbb{R}^n$ that passes through each point (this hyperplane does not intersect the origin).
Under this geometric interpretation, $A^{-1}$ has an interesting property: the normal vector to the hyperplane is given by the row sums of $A^{-1}$ (i.e. $A^{-1} \cdot 1$, where $1 = \langle 1, \dots, 1 \rangle^T$).
Within this geometric interpretation of $A$, what other interesting properties does $A^{-1}$ have? Do the individual entries of $A^{-1}$ have geometric meaning? How about the column sums?