I hope it can help you
DFA that accepts strings having an odd number of $1$'s:
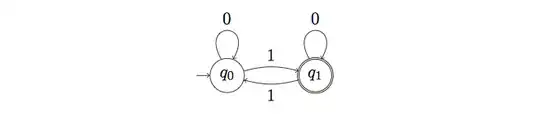 There are several methods for reading a regular expression from a DFA. If we use the state removal technique:
There are several methods for reading a regular expression from a DFA. If we use the state removal technique:
this DFA are in Final form ,
regular expression for DFA is : $0^*1(0+1{0}^*1)^*$
Brzozowski Algebraic Method using Arden's Theorem
Note that when we apply Arden's theorem, the transition graph does not
have $\epsilon-moves$ and it should have only one initial state, say
$N_1$.
- its vertices are $N_1,N_2,....N_n.$
- $N_i$ is the regular expression representing the set of strings accepted by the system even though $V_i$ is finial state.
- $\alpha_{ij}$ denotes the regular expression representing the set of labels of edges from $N_i$ to $N_j$,when there is no such edge,
$\alpha_{ij}=\emptyset$
consequently, we can get the set of equations.here $\epsilon$ should
be added in the equation of initial state $N_1$, i.e.
\begin{align} &N_1=N_1\alpha_{11}+N_2\alpha_{21}+ ...
+N_n\alpha_{n1}+\epsilon \\ &N_2=N_1\alpha_{12}+N_2\alpha_{22}+ ... +N_n\alpha_{n2} \\ .\\ .\\ .\\ &N_n=N_1\alpha_{1n}+N_2\alpha_{2n}+ ... +N_n\alpha_{nn} \\ \end{align}
by repeatedly applying substitution and Arden's theorem, we get $N_i$
in terms of $\alpha_{ij}$'s.if there are more final states,then we have
to take the union of all $N_i$'s corresponding to the final states.
"Introduction to Automata and Compiler Design - Dasaradh Ramaiah K."
If we use the Brzozowski Algebraic Method:
\begin{align}
&q_0=q_00+q_11+\epsilon \\
&q_1=q_01+q_10
\end{align}
by Arden's theorem ($r=rp+q$ has only solution $r=qp^*$) for $q_1$ we have:
\begin{align}
&q_1=q_010^* \tag{1}
\end{align}
\begin{align}
&q_0=q_00+q_010^*1+\epsilon \\
&\,\,\,\,\,=q_0(0+10^*1)+\epsilon
\end{align}
by Arden's theorem for $q_0$ we have:
\begin{align}
&q_0=(0+10^*1)^* \tag{2}
\end{align}
final regular expression is: $$(0+1{0}^*1)^*10^* \tag{1,2}$$
