Plot integrand for few values of $x$:
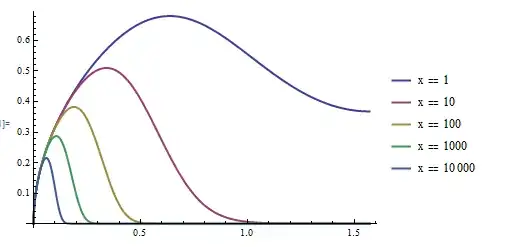
It is apparent that the maximum shifts closer to the origin as $x$ grows.
Let's rewrite the integrand as follows:
$$
\int_0^{\pi/2} \sqrt{\sin(t)} \exp\left(-x \sin^4(t)\right) \mathrm{d}t = \int_0^{\pi/2} \exp\left(\frac{1}{2} \log(\sin(t))-x \sin^4(t)\right) \mathrm{d}t
$$
The maximum of the integrand is determined by
$$
0 = \frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}t} \left(\frac{1}{2} \log(\sin(t))-x \sin^4(t)\right) = \cot(t) \left( \frac{1}{2} - 4 x \sin^4(t)\right)
$$
that is at $t_\ast = \arcsin\left((8 x)^{-1/4}\right)$. Then using Laplace's method:
$$
\int_0^{\pi/2} \sqrt{\sin(t)} \exp\left(-x \sin^4(t)\right) \mathrm{d}t \approx \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \exp\left(\phi(t_\ast) + \frac{1}{2} \phi^{\prime\prime}(t_\ast) (t-t_\ast)^2 \right) \mathrm{d}t = \exp\left(\phi(t_\ast)\right) \sqrt{\frac{2\pi}{-\phi^{\prime\prime}(t_\ast)}}
$$
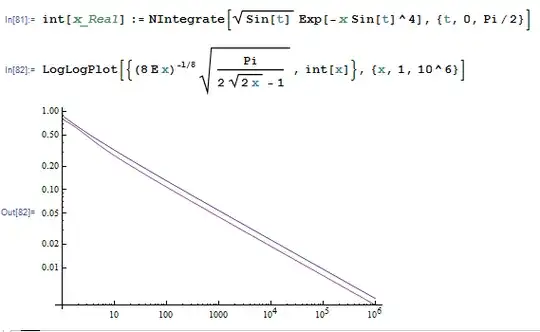
Easy algebra gives $\exp\left(\phi(t_\ast)\right) = (8 \mathrm{e} x)^{-1/8}$, $-\phi^{\prime\prime}(t_\ast) = 4 \sqrt{2 x} - 2$, giving
$$
\int_0^{\pi/2} \sqrt{\sin(t)} \exp\left(-x \sin^4(t)\right) \mathrm{d}t \approx (8 \mathrm{e} x)^{-1/8} \sqrt{ \frac{\pi}{2 \sqrt{2 x} -1}}
$$