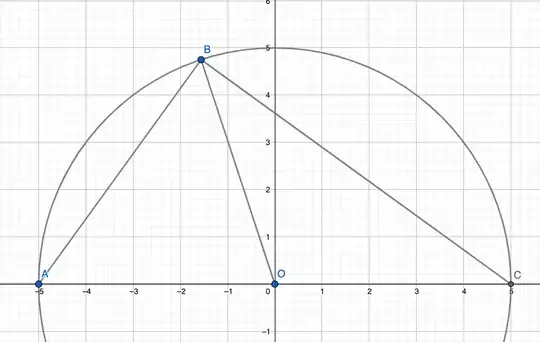
The area of triangle $ABC$ is just $\Delta ABO + \Delta BOC$. If $\angle BOC = \theta$, the area is:
$$\frac{1}{2} r^2 \sin \theta + \frac{1}{2}r^2 \sin(180 - \theta) = \frac{1}{2}r^2 \big( \sin \theta + \sin(180 - \theta) \big) = \frac{1}{2}r^2 (2 \sin \theta) = r^2 \sin \theta$$
where we have used the identity $\sin \theta = \sin(180 - \theta)$.
The maximum value of $\sin \theta$ is $1$, so the maximum area is $r^2$. In this case, $r = 5$ so the maximum area is $25$.
This occurs when $\theta = \frac{\pi}{2}$ or $90º$, so $\Delta ABC$ must in fact be isoceles.
Alternatively, if $A = (-5,0)$, $B = (5 \cos t, 5 \sin t)$, $C = (5,0)$, then the area of $\Delta ABC$ using the shoelace formula is:
$$
\begin{vmatrix}
5 & 0 \\
5 \cos t & 5 \sin t \\
-5 & 0 \\
5 & 0 \\
\end{vmatrix}
$$
so the area is: $$\frac{1}{2} \big((25 \sin t + 0 + 0) - (0 + -25 \sin t + 0) \big) = 25 \sin t$$
which takes the maximum value $25(1)$ when $t = \frac{\pi}{2}$, again.
The area of triangle $ABC$ is can also be computed using determinants:
$$
\begin{vmatrix}
5 & 0 & 1 \\
5 \cos t & 5 \sin t & 1 \\
-5 & 0 & 1 \\
\end{vmatrix}
$$
which when computed, gives:
$$\frac{1}{2} \left((25 \sin t + 0 + 0) - (-25 \sin t + 0 + 0) \right) = 25 \sin t.$$